Gastric Bypass
Consultations offered at our three convenient locations in Pomona, Rancho Cucamonga and Apple Valley, CA

The gastric bypass is the gold standard bariatric procedure for massive weight-loss. The most common method is the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB), a technique that makes small incisions in the abdomen, through which the surgeon reduces the size of the stomach to a small pouch, roughly the size of a large egg. The pouch that remains connects directly to the second part of the small intestine, completely bypassing the first section.
Obesity is an ongoing problem for millions of Americans. Among the many serious effects it has, it can lead to secondary health concerns, limit mobility, and greatly affect self-esteem and social acceptance. A bariatric procedure greater control over food intake, enabling effective long-term weight loss and the prospect of living a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Pacific Med Health Group provides a range of interventions to help patients reduce the amount of food they consume and lower their Body Mass Index (BMI). These include the gastric bypass, gastric sleeve, lap band, and gastric balloon. And with over 33 years of experience, board-certified bariatric surgeon Dr. Lee Au uses his years of experience in the field to create the most effective treatment plan to help you. We have three offices in Southern California, in Pomona, and Apple Valley to serve the residents of LA County, San Bernardino County, and the Inland Empire. Call (800) 555-5551 to book an appointment at your nearest location, or make your request for a personal consultation online.
Contents
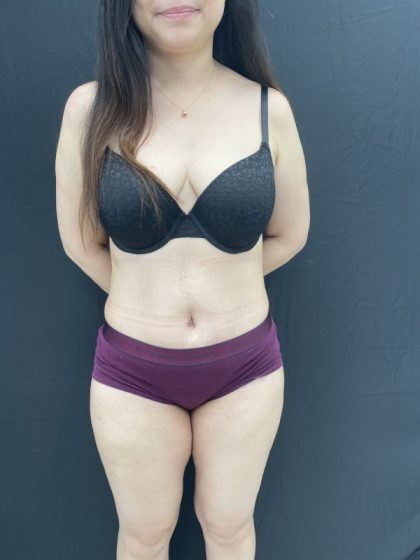
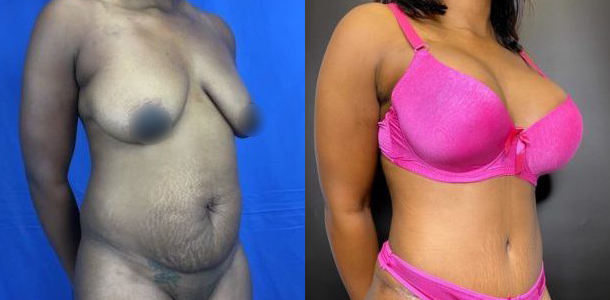
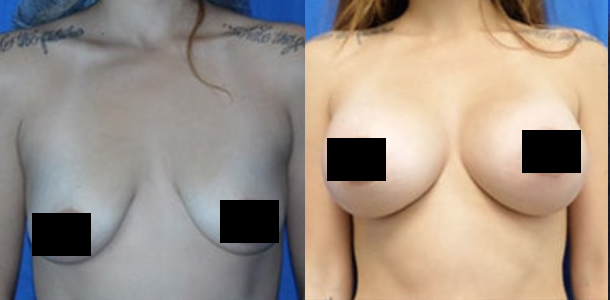
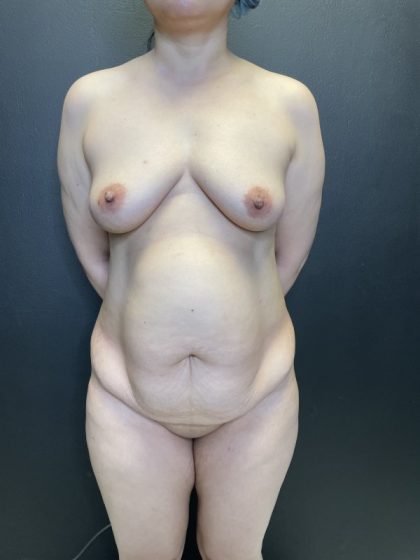
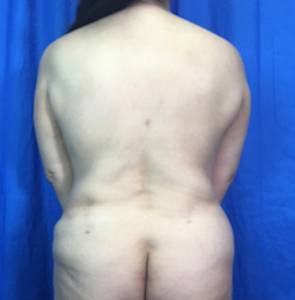
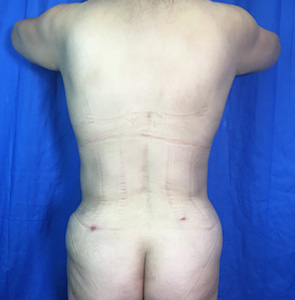
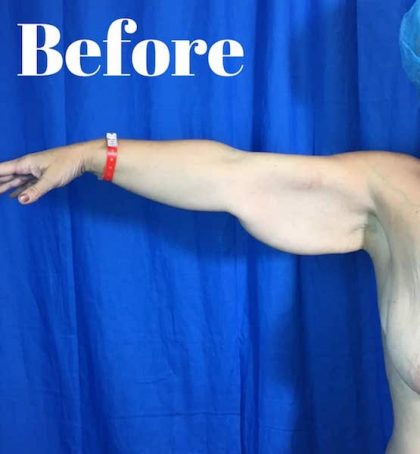
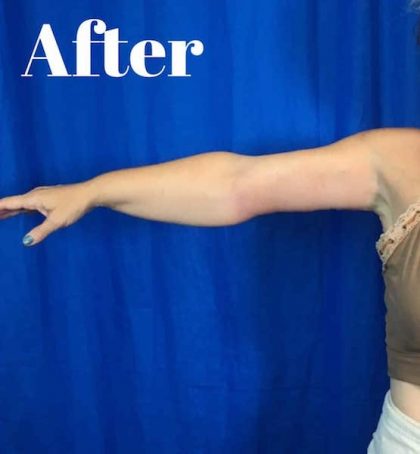
Before and After Photos
Obesity Health Concerns
Almost 79 million Americans have a BMI that is classified as obese. Although the “diet and exercise” mantra may be repeated frequently by healthcare professionals, for many people efforts to lose weight can produce disappointing results in long-term weight management. (1)
RYGB surgery is indicated for overweight individuals with a BMI of over 40, or people with obesity-related comorbidity and a BMI of 35 or more. Consistent data shows that individuals who are very overweight are at a far higher risk for life-limiting and life-threatening conditions and diseases. These include the following.
Other life-limiting physical changes from excess fat can also occur, including the following.
- Mobility Issues
- Stretch Marks
- Swollen Feet
- Gynecomastia (Male Breast Development)
- Hirsutism (Abnormal Female Hair Growth) (2)
- Skin Tags
- Acne
- Hernias
- Stasis Dermatitis
What Causes Obesity?
The simplest way to explain the cause of obesity is as an imbalance between the amount of energy consumed and the amount of energy expended by an individual. If we do not burn off the necessary amount of calories every day, our body stores this energy as fat throughout the body, especially in the abdomen, buttocks, thighs, and hips. Our genetics, diet in early life, sleep patterns, stress, health conditions, and medications are also factors in the way we store fat and how much weight we gain.
About Gastric Bypass Surgery
Between 60-70% of all bariatric procedures are gastric bypasses. (1) First developed in the 1970s by Dr. Edward E. Mason, (3) the procedure has since helped millions of people get to a healthier weight, decrease their risk of developing an obesity-related disease, and achieve a better overall quality of life.
There are three ways that this surgery is performed: open, laparoscopic, and robotic. The type of procedure chosen is based on the preferences of the surgeon and the individual risks associated with the surgery for the patient. Additionally, although gastric bypass is incredibly effective, patients must meet strict criteria to be eligible.
The Digestive System
The digestive system is made up of the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract), the liver, the pancreas, and the gallbladder. Each part of the system functions to digest food and break it down into vital nutrients before expelling unwanted and unused materials as waste. Smooth muscle, an involuntary muscle type, contracts and relaxes in a process called peristalsis to move food matter through the system. The GI tract has many sections, as listed below.
- Mouth
- Pharynx (Throat)
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Large Intestine
- Rectum
- Anus
Bariatric surgeons access and alter two targeted areas of internal abdominal anatomy during a gastric bypass, the stomach and the small intestine. A list of terms that may be unfamiliar to patients is below.
Glossary of Anatomical Terms
Duodenum – The first section of the small intestine connected to the lower stomach.
Jejunum – The second part of the small intestine that connects to the duodenum at one end and the large intestine at the other. A jejunojejunostomy is part of the gastric bypass process and involves making an anastomosis (a cross-connection between two channels) between two sections of the jejunum.
Formulation of the “Y” Shape:
Roux Limb – The medical term for the bypassed section of the small intestine. It is kept in position to supply bile for digestion and is not removed. Also called the Biliopancreatic limb.
Alimentary/Nutrient Limb – The remaining part of the small intestine connected to the stomach pouch and large intestine.
Common Channel – The portion of remaining small intestine that empties into the large intestine after bile from the biliopancreatic limb has helped to break down fats.
Benefits of Gastric Bypass Surgery
- Up to 60% excess weight loss expected (4)
- Long-term improvements in co-morbid conditions
- Permanently reduces the physical ability to eat in excess
- Helps you lose weight safely and quickly
- Improved self-esteem and body image
- 92% lower risk of death from diabetes (5)
- Risk of death from any related medical condition reduced by 40% (5)
Candidates for Gastric Bypass Surgery
Gastric bypass surgery is for patients between 18-65 years of age with a BMI over 40, and patients with a BMI over 35 with related comorbid medical conditions. Research indicates that bariatric procedures may be available to patients over 65, and surgeons consider risks and benefits on a case-by-case basis. (6) Patients who wish to undergo a gastric bypass procedure must agree to a comprehensive evaluation of their condition by medical professionals before the procedure can be scheduled.
For more information about bariatric surgery at Pacific Med Health Group, please read our blog.
Bariatric Consultations
An initial consultation at Pacific Med Health Group will walk you through the preparatory stages of gastric bypass surgery. Our staff knows the stress and discomfort excess weight causes, and will treat you with compassion and understanding throughout your treatment. We will ask you to provide some information about your general health, as well as the details of any prior treatment you have received in relation to your weight. If you have other conditions as a result of excess weight, please be ready to answer questions about them. It may take more than one appointment with us as well as appointments with other medical professionals to collect all of the necessary information. These include the following.
- Psychological evaluation
- Nutritional evaluation
- Creation of a preoperative weight-loss plan
- Medical clearance
- Preoperative ultrasound (7)
Patients with significant gastrointestinal symptoms may require an esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), a procedure that examines your GI tract from the esophagus to the duodenum with an endoscope. (7)
Preparation and Recovery
Bariatric surgery involves significant preparation on the part of the patient, and a clear understanding of the recovery process and the new life changes necessary to achieve the most effective results. Dr. Au will provide detailed written instructions regarding preparation and aftercare once your procedure has been confirmed to ensure you are 100% ready for your weight-loss surgery.
The Gastric Bypass Procedure
Laparoscopic gastric bypass surgery involves small access points called ports, whereas open surgery involves the placement of a long vertical incision down the center of the abdomen. Dr. Au lifts an apron of tissue called the greater omentum to access the digestive tract. Using precise surgical techniques, and specialized surgical instruments the following stages are completed.
- Creation of the Roux limb
- Jejunojejunal anastomosis
- Creation of gastric pouch
- Gastrojejunal anastomosis
- Endoscopy
- Closure of access point(s) (4)
Following gastric bypass surgery, patients can expect to see a noticeable decrease in their weight. You will see the most significant weight-loss in the first 12-24 months following the procedure. Most patients lose between 50-60% of their excess weight and continue to keep it off with results that last. This provides relief from many of the life-limiting physical and mental effects of excess weight, and allows patients a “new lease” on life!
Cost of Gastric Bypass Surgery
All bariatric procedures require a detailed patient assessment and collaboration with other professionals outside the bariatric team. In many cases, health insurance providers will cover medical costs if certain criteria are met. Use our free insurance verification tool to find out more about your coverage. Book your initial consultation with Dr. Au by calling (800) 555-5551 or by filling out this convenient form to start your journey toward a healthier weight!
References
- Mitchell BG, Gupta N. Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. PubMed. Published 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553157/
- Panuganti KK, Nguyen M, Kshirsagar RK. Obesity. PubMed. Published 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459357/#:~:text=Obesity%20is%20associated%20with%20cardiovascular
- Wolfe BM, Kvach E, Eckel RH. Treatment of Obesity. Circulation Research. 2016;118(11):1844-1855. doi:10.1161/circresaha.116.307591 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4888907/
- Seeras K, Philip K, Baldwin D, Prakash S. Laparoscopic Gastric Bypass. PubMed. Published 2022. Accessed October 12, 2022. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK518968/#:~:text=Patients%20can%20expect%20to%20have
- Benefits of Bariatric Surgery | ASMBS. American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery. https://asmbs.org/patients/benefits-of-weight-loss-surgery
- Susmallian S, Raziel A, Barnea R, Paran H. Bariatric surgery in older adults. Medicine. 2019;98(3). doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000013824 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6370135/#:~:text=In%201991%2C%20the%20National%20Institutes,ideal%20for%20performing%20bariatric%20surgery.
- Benalcazar DA, Cascella M. Obesity Surgery Pre-Op Assessment And Preparation. Nih.gov. Published September 14, 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK546667/